When we check and filter out the duplicates for a web crawler, bloom filter is a good choice to curtail the memory cost. Here is a brief introduction.
Bloom filter
Bloom filter is a space-efficient probabilistic data structure to test the existence of an element. The response of bloom filter for each query is either “possibly in set” or “definitely not in set”.
- Drawbacks: Elements inside the set can be supplemented, but cannot be removed. “The more items added, the larger the probability of flase positives.”[1]
Algorithms
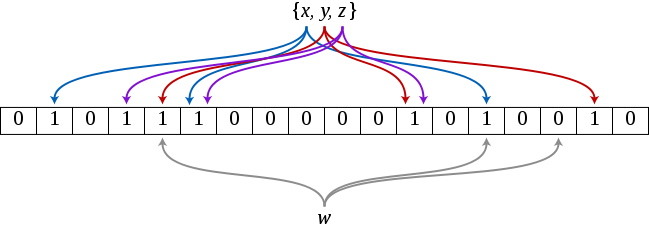
An empty bloom filter is a 1d boolean array with a length of $m$. In addition, $m$ different hash function are used to map the input query elements to one of the $m$ bits.
To query for an element, it firstly computes $k$ hash values with different hash functions, and then divides $m$ to get $k$ remainders, indicating $k$ positions in the array.
- If any of the bits at these positions is 0, it means the element is definitely not in the set. Fill out the corresponding position with 1s when the element is added.
- If all of the mod bits are 1, there are two possiblities:
- True positive: the element is already in the set
- False positive: bits have by chance been set to 1 during the insertion of other elements.
- Let $n$ be the # of elements, the flase positive probability $\epsilon$, the array length $m$ should be (see [1] for the derivation):
Code
1 | def Bloomfilter(filter: "bit array", value: "elements", hash_fns: "hash functions"): |
